If you are managing SEO across multiple business locations, you already know that traditional checklists don’t scale. What works for one store often breaks when applied to five, fifty, or five hundred. From inconsistent listings to fragmented reviews and overlapping service areas, multi-location local SEO brings operational challenges that most guides overlook.
This post brings a strategy built around how today’s consumers search, choose, and trust local businesses like yours. Whether you are expanding across cities or managing different branches in one city, you will get a framework that’s scalable, role-aware, and execution-ready.
Why Local SEO Gets Complicated With Scale
Local SEO is about visibility in location-based searches, but when your client has several stores, it creates new challenges:
- Inconsistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) data
- Duplicate listings
- Conflicting reviews and user-generated content
- Overlapping service areas
- Disjointed Google Business Profiles (GBP)
Search engines thrive on accuracy and consistency. When your business locations aren’t aligned in how they’re presented online, it creates confusion—for both algorithms and users.
12 Actionable Local SEO Strategies for Businesses with Multiple Locations
In today’s digital landscape, local SEO is crucial for businesses with multiple locations to stand out in their respective markets. The following 12 proven strategies will help you enhance your online presence and drive more customers to each of your locations.
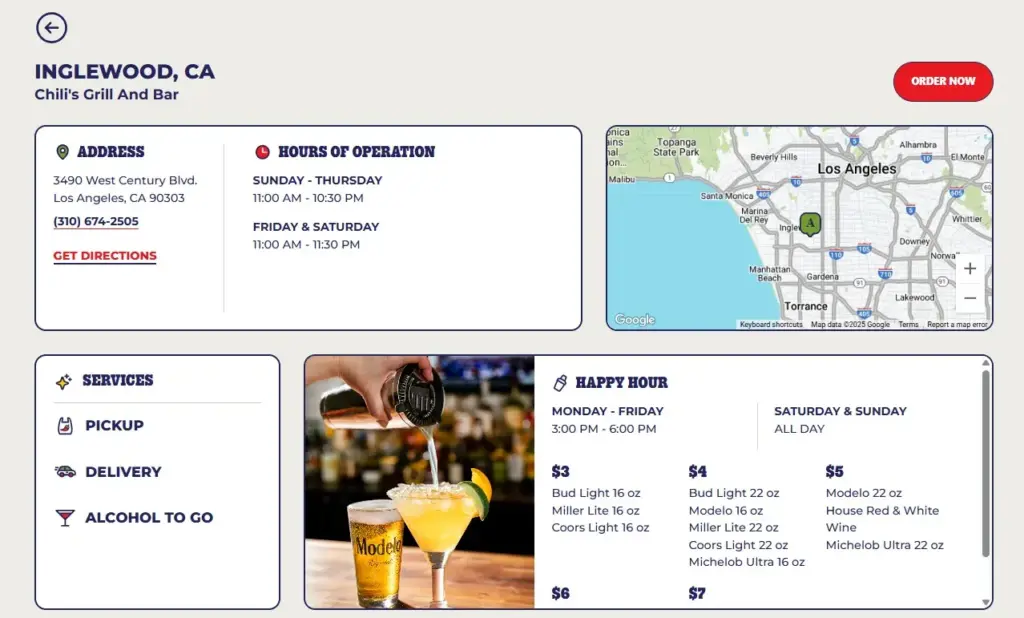
1. Set Up and Manage Your Google Business Profile
Each GBP listing must be claimed, verified, and optimized with location-specific data on business hours, categories, and high-quality photos. Here’s what you need to get right:
- Claim and verify every GBP listing – No matter how many locations you have, each one needs its own verified profile to appear in local searches and Maps. You can also verify multiple business locations in bulk.
- Use location-specific categories – If each store offers slightly different services or products, reflect that in the categories and highlights you choose.
- Upload unique photos per location – Real storefront images and staff photos improve engagement and reduce bounce rates from profile views.
- Phone number & directions – Ensure that each location has the correct phone number and an accurate map pin.
A well-structured GBP setup is the starting point for any local SEO for multiple locations, especially when your brand appears in overlapping markets or high-density areas.
2. Create Location-Specific Landing Pages
Generic location lists don’t do much for visibility—or for user experience. If you want each store to rank locally and connect with nearby customers, build a dedicated landing page for every location.
Each page should include:
- Localized keywords that reflect how people in that area search (e.g., “jewelry store in Austin downtown” instead of just “jewelry store”)
- Accurate NAP info—that’s Name, Address, Phone Number—along with an embedded Google Map
- Optional extras like the local manager’s name or store hours to build trust
- Testimonials or reviews from customers in that specific location
- Location-based blog posts or updates that show you’re active and relevant in that community
Example: Skip the catch-all “/locations” page. Instead, go for URLs like /new-york-midtown/ or /austin-downtown/, each with tailored content that reflects the unique character and needs of that area.
This structure helps your pages rank better in local search and gives customers the confidence they’re in the right place—both online and in-store.
3. Use Schema Markup Across Locations
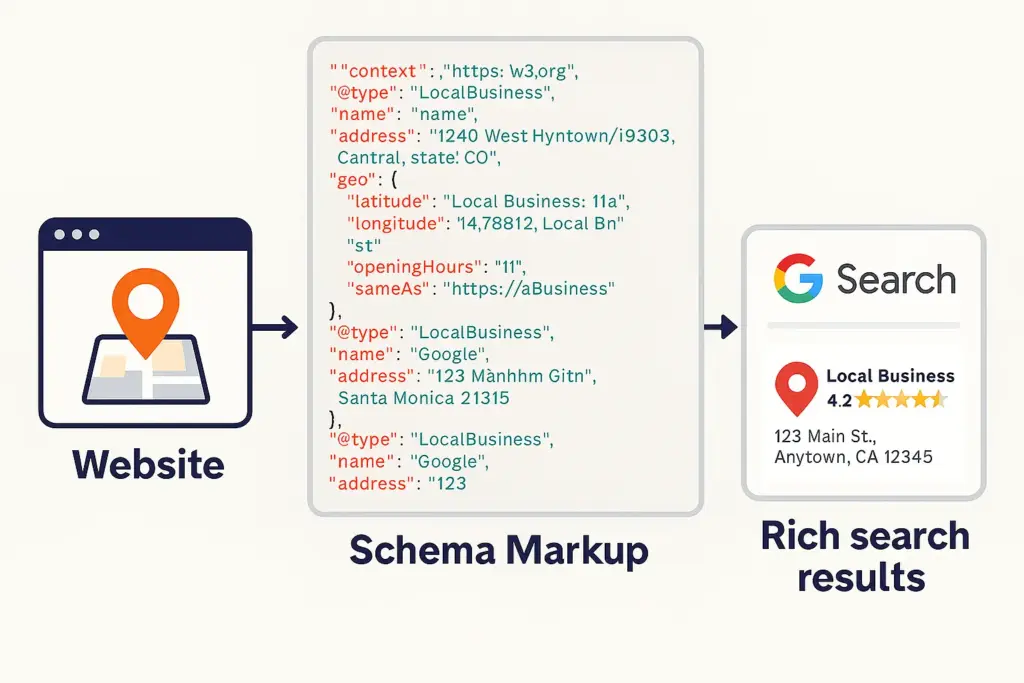
You need clean HTML and structured data to help search engines better understand your location pages. That’s where schema markup comes in. If you are running multiple branches, here’s how you apply it with precision:
- Add the LocalBusiness schema on every store page. For example, your Delhi page should include “@type”: “LocalBusiness”, and include structured fields like “address”, “geo” (latitude/longitude), and “openingHours”.
- Apply JSON-LD via your CMS using dynamic variables. For example, in Shopify or WordPress with RankMath, you can populate location schema by pulling in the city name, phone number, and coordinates from your store database. This saves time across 50+ locations.
- Validate every schema using Google’s Rich Results Test, not just once but every time your page updates. Even a missing comma can break rendering.
- Add high-quality, geo-tagged images with descriptive alt text. These support visibility in Google’s visual search and future AI-generated SERPs.
In 2025, structured data is foundational to any local search engine optimization strategy that spans across dozens or hundreds of business website pages.
4. Encourage and Manage Location-specific Reviews

Scaling review generation isn’t about getting more stars. It’s about building localized trust signals that improve conversion, rankings, and map pack visibility.
Here’s your step-by-step playbook:
- Retail locations: Train your store staff to offer QR codes tied to Google review URLs at checkout.
- Clinics or appointment-based businesses: Trigger review requests via SMS or email 2–3 hours post-visit. The review generation tool by GMB Briefcase can automate this by integrating with your business listing.
- Service businesses: Add review prompts at the final touchpoint (e.g., after a technician closes a ticket). Pre-approve language with your legal/compliance team if needed.
Now, what about responses?
- Assign reply responsibility: Store managers or field reps should respond directly. Use an automated review response tool where your team can manage reviews, reply to them with personalization from a single dashboard.
Use templated response kits. For example: “Thanks, [Name]! We’re thrilled your [City] experience met expectations.” Or: “Sorry to hear about the wait time. We’ve flagged this to [Location]’s team lead and will follow up.”
5. NAP Audit and Consistency
When your business spans dozens or hundreds of locations, your Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) details must remain identical across every platform. Even a minor inconsistency (like “St.” vs “Street”) can break trust with search engines and drag down your local visibility.
Consider GMB Briefcase or any other local SEO software for centralized location management to streamline this at scale. Using local SEO tools you can easily sync accurate data across dozens of directories in one push, saving you from chasing down each site manually. Export your master location data, scan for mismatches, and fix listings on high-authority sites like Google, Yelp, and Bing first.
Let the main offices manage a master NAP sheet while field teams submit change requests. Consistent NAP information improves local visibility and your chances of ranking in the search and maps, prevents search suppression, and builds brand consistency across every touchpoint.
6. Build Local Authority with Smart Backlinks
Backlinks matter, yet relevance and locality outweigh volume in multi-location SEO. A store-level link from a Chamber of Commerce or local newspaper often brings more SEO value than 10 generic blog mentions. To build high-authority, location-relevant backlinks:
- Prioritize hyperlocal links – Sponsor city-level events, community fundraisers, or local trade shows. These build trust and earn contextual .org/.edu backlinks.
- Use store manager involvement – Encourage each branch to engage in its own partnerships (e.g., local gyms, schools, associations).
- Leverage citations from niche directories – For example, list a dental clinic on Healthgrades, a salon on JustDial, or a restaurant on Zomato/TripAdvisor.
- Centralize link-building playbooks – Create templates that regional teams can adapt for their city (e.g., pitch emails, outreach scripts).
- Proximity – A backlink from “Chicago News Journal” to your Chicago location page is 10x more potent than a generic guest post.
- Focus on quality, not quantity: Scaling backlinks across 100+ locations introduces risk: repetitive anchor text, domain overlap, or unnatural link velocity can trigger algorithm penalties.
These tactics help you build local search authority at the individual store level, which supports both Google’s local 3-pack rankings and organic visibility.
7. Combining National and Local Authorities for Better Outcomes
Strong SEO performance for multi-location businesses comes from balancing national PR strength with hyperlocal credibility and signaling through your backlink profile.
To blend both effectively:
- Use national press for brand visibility – Coverage from TechCrunch, Economic Times, or major PR media builds your domain trust.
- Pair PR with location-level linkbacks – For each PR placement, pitch regional partners too. Example: After a national funding story, encourage local news in each city to cover “new store opening” angles.
- Use internal links to route authority – Link from national press releases or brand blogs to high-priority location pages to pass link equity intelligently.
This hybrid approach prevents over-reliance on local citations and helps future-proof your local SEO strategy for multiple locations, especially in competitive metro areas.
8. Playbooks for Location-specific Content Templates
At scale, content needs to be more than just custom-written for every page; it can’t be copied either. You need a content playbook that defines which elements stay fixed and which are localized. Build more innovative templates by separating:
Static elements – These stay the same: product/service descriptions, brand tone, design blocks, CTA structures.
Dynamic/localized elements
These change per location:
- Page title and meta tags (e.g., “Dental Clinic in Hyderabad – XYZ Dental”)
- Top 1–2 paragraphs with location-specific context
- Embedded reviews from that branch’s GBP
- Local events, team member bios, or neighborhood highlights
For multilingual regions, localize not just language but tone and phrasing (e.g., “clinic” vs “medical centre”) using “hreflang” tags for translated content.
Keep a shared content matrix across teams so local managers know what they can change and what’s locked. When templates are done right, you maintain brand consistency while ensuring every store’s page delivers unique value to users and search engines.
9. Hub-and-Spoke Content Models Across Cities or States
As your locations expand, content silos can dilute your SEO impact. A hub-and-spoke model helps consolidate authority while giving each area its unique space. How to structure it:
- Create a city or regional “hub” page — e.g., “Dental Clinics in New York.”
- Link spokes for each branch like “Williamsburg,” “Harlem,” and “SoHo” pages under the Mumbai hub.
- Use internal linking between spokes when nearby (e.g., “Find other locations near Harlem”).
- Ensure store locator pages use crawlable, static URLs (e.g., /stores/williamsburg) and link each spoke to its own indexable page with schema.
This structure deepens topical authority by clustering related content and helps Google recognize the parent-child relationship between regions and branches, which is essential in a multi-location local SEO.
10. Injecting Local Storytelling to Avoid Duplicate Thin Pages
No two branches serve customers exactly the same, which your content must reflect. Local storytelling transforms templated pages into human-first experiences.
- Customer reviews pulled from the branch’s Google profile — “Loved the staff at the Indiranagar clinic—super clean and quick!”
- Team bios and store photos — “Meet Katie, our London branch manager with 12 years in orthodontics.”
- Mentions of neighborhood events — “We proudly supported the Miami Beach Clean-Up Drive in July 2025.”
This type of content can’t be faked, and that’s precisely why search engines (and your customers) trust it. It’s one of the best SEO strategies for local multi-location businesses who want to rank without duplicating.
11. How to Measure SEO Success by Location?
Scaling local SEO means measuring performance branch by branch. Track these key metrics per location:
- Business profile interactions and views
- Calls, directions, website clicks and bookings
- Review volume + rating velocity
- Keyword visibility for geo-modified terms – Track “plumber in Austin” vs “plumber near me” per page
- Organic traffic to each location page – Use UTM tags or filtered views in GA4
Use a geo-grid rank tracker to compare your GBP visibility against nearby competitors for the exact service keywords.
12. Reporting Dashboards by Stakeholder (HQ vs. Field Teams)

One report might not work for everyone. Your dashboards should match what each team needs to act on, not overwhelm them with data. Split reporting like this:
HQ teams
- See big-picture patterns across locations
- Compare top vs. low performers
- Monitor brand-wide NAP consistency and review distribution
- Prioritize budgets or support based on trends
Local teams/store managers
- View their location’s live rankings, calls, and reviews
- Get review alerts for timely replies
- Access location-specific content performance (CTR, bounce rate)
Use local SEO software or analytics tools to generate clean, role-specific dashboards. This alignment lets every team focus on the SEO levers they control, across locations.
Scaling local SEO means measuring performance branch by branch. Track these key metrics per location:
- Business profile interactions and views
- Calls, directions, website clicks and bookings
- Review volume + rating velocity
- Keyword visibility for geo-modified terms – Track “plumber in Austin” vs “plumber near me” per page
- Organic traffic to each location page – Use UTM tags or filtered views in GA4
Use a geo-grid rank tracker to compare your GBP visibility against nearby competitors for the exact service keywords.
Build Systems, Not Just SEO Wins
Local SEO is more about building repeatable, governed systems that work whether you have five branches or five hundred than just about optimizing listings or creating content. Throughout this guide, you have seen how to:
- Optimize Google Business Profiles and pages to avoid overlap.
- Use schema and NAP governance to strengthen trust signals.
- Create location content that’s unique, scalable, and story-driven.
- Build authority through both local links and national brand PR.
- Assign roles, track KPIs, and use dashboards that serve both HQ and store managers.
And as consumer search evolves, don’t just optimize but observe. Track competitors, embrace AI shifts, and prepare your systems for what’s next. It will come from doing it brighter, cleaner, and more consistently than your competitors. Your next steps: Audit → SOP → Assign → Automate. That’s the formula for scalable multi-location local SEO and sustainable growth.
FAQs
Q1. Can I use one Google Business Profile for all my locations?
Ans: No. Google requires a separate GBP for each physical location you serve. Using one profile for multiple locations violates their guidelines and prevents you from ranking in the local Map Pack for each area. Instead, claim and verify each GBP individually, optimize them with location-specific data, and manage them through Google Business Profile Manager.
Q2. Can I target multiple neighborhoods in one city with local SEO?
Ans: Yes, but only if each location serves a distinct area. You will need individual pages and GBPs optimized with neighborhood-specific keywords, reviews, and content. Use hub-and-spoke models: create a city-level hub (e.g., “Gyms in Mumbai”) and link to subpages like “Andheri Gym” or “Bandra Gym.”
Q3. How do I track local SEO performance for each location?
Ans: Use tools like Google Business Profile Insights or GMB Briefcase to track location-level performance. With this local SEO tool you can easily manage multiple Google Business listings, create customized reports to see actionable insights and more.